A Unified TinyML System for Multi-modal Edge Intelligence and Real-time Visual Perception.
 A Unified TinyML System for Multi-modal Edge Intelligence and Real-time Visual Perception
A Unified TinyML System for Multi-modal Edge Intelligence and Real-time Visual Perception1. Introduction
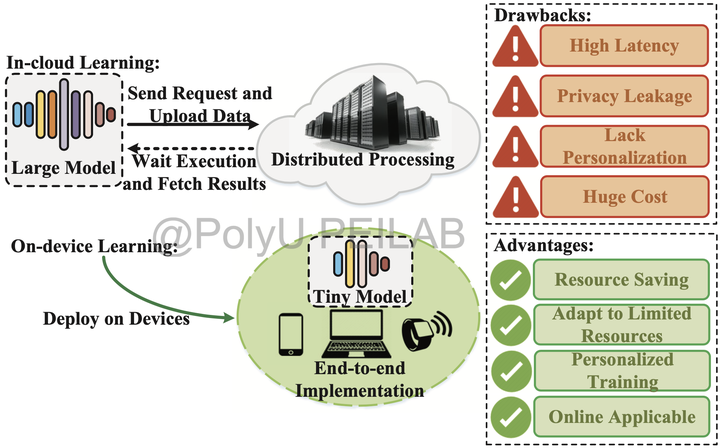
Modern machine learning (ML) applications are often deployed in the cloud environment to exploit the computational power of clusters. However, this in-cloud computing scheme cannot satisfy the demands of emerging edge intelligence scenarios, including providing personalized models, protecting user privacy, adapting to real-time tasks and saving resource costs. To conquer the limitations of conventional in-cloud computing, it comes the rise of on-device learning, which handles the end-to-end ML procedure mainly on user devices, and restricts unnecessary involvement of the cloud. Despite the promising advantages of on-device learning, implementing a high-performance on-device learning system still faces many severe challenges, such as insufficient user training data, backward propagation blocking and limited peak processing speed.
Illustration: Conventional ML applications rely on the in-cloud learning paradigm, incurring essential drawbacks. Upgrading to the TinyML paradigm can effectively address these issues.
2. Architecture Overview
Observing the substantial improvement space in the implementation and acceleration of on-device learning systems, our group devote to designing high-performance TinyML architectures and relevant optimization algorithms, especially for embedded devices and microprocessors. Our research focuses on the software and hardware synergy of on-device learning techniques, covering the scope of model-level neural network design, algorithm-level training optimization and hardware-level instruction acceleration. Here, we present the architecture overview of our system design.
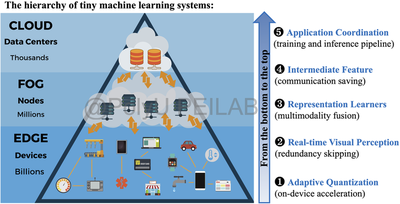
Illustration: an efficient TinyML system require a holistic design of the entire hierarchy, which can be resolved as five key research opportunities.
3. Research Opportunities
Here are five key research opportunities to implement our system. Please check the sub-folders for details.
4. Achievements
The on-device learning techniques can be employed in many emerging TinyML scenarios, where the system performance is often bounded by the limited hardware resources. Currently, our group has achieved breakthroughs in improving the computational capacity and designing domain-specific AI chips for task acceleration. These chips can be designed from the perspectives of model compression, few-shot learning, quantization-ware training, memory management and low-level instructions. We pursue the vision that helps researchers and developers optimize AI deployment without tedious code modifications. Some research demos have been open-source on Github, please visit at:
5. Related Publications
[1] Octo: INT8 Training with Loss-aware Compensation and Backward Quantization for Tiny On-device Learning, In Proc. of USENIX Annual Technical Conference (ATC), 2021 (CCF-A). [2] On-device Learning Systems for Edge Intelligence: A Software and Hardware Synergy Perspective, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020 (JCR-Q1). [3] Petrel: Heterogeneity-aware Distributed Deep Learning via Hybrid Synchronization, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems (TPDS), 2020 (CCF-A). [4] Dual-view Attention Networks for Single Image Super-Resolution, In Proc. of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM), 2020 (CCF-A).
6. Cooperators
Our group have established close cooperation with industrial communities, including Microsoft Research Asia, Alibaba DAMO Academy, Huawei Cloud, etc.
7. PhD/intern Applications:
We are looking for students and partners who are interested in:
(1) On-device/TinyML Systems (for Edge Intelligence)
(2) Distributed Machine Learning Systems (for Data center)
(3) Modern AI/ML frameworks: e.g., NVIDIA NCCL, CUDA, TensorRT, Apple CoreML, PyTorch, TensorFlow, Keras, BytePS, Gym, etc.
(4) Domain-specific hardware optimization and implementation, e.g., NVIDIA Jetson, FPGA, Microprocessors, AI Chips, etc.
(5) Coding contribution to our GitHub repositories.